
After gathering all the requirements from our customer and analysing over them as a team, we moved on to the next phase. In the System Design phase, the different functionalities of the application were represented as UML diagrams.
Behavior Diagrams
For every operation within the app, it’s respective Behavioral diagram was drawn. This basically denoted a ‘Start’, ‘Operation’ and ‘Stop’ stage. This gives a detailed analysis over the sequence of actions. The flow of each operation was represented under this Behavior Diagrams.
Also, since there could be mutiple operations, one foreground activity might, after completing its defined operation, stay and work on the background for another activity to run in the foreground. These cases of parallel processing were represented. An insight over multiple users operating on the app, was studied.
Add a new activity
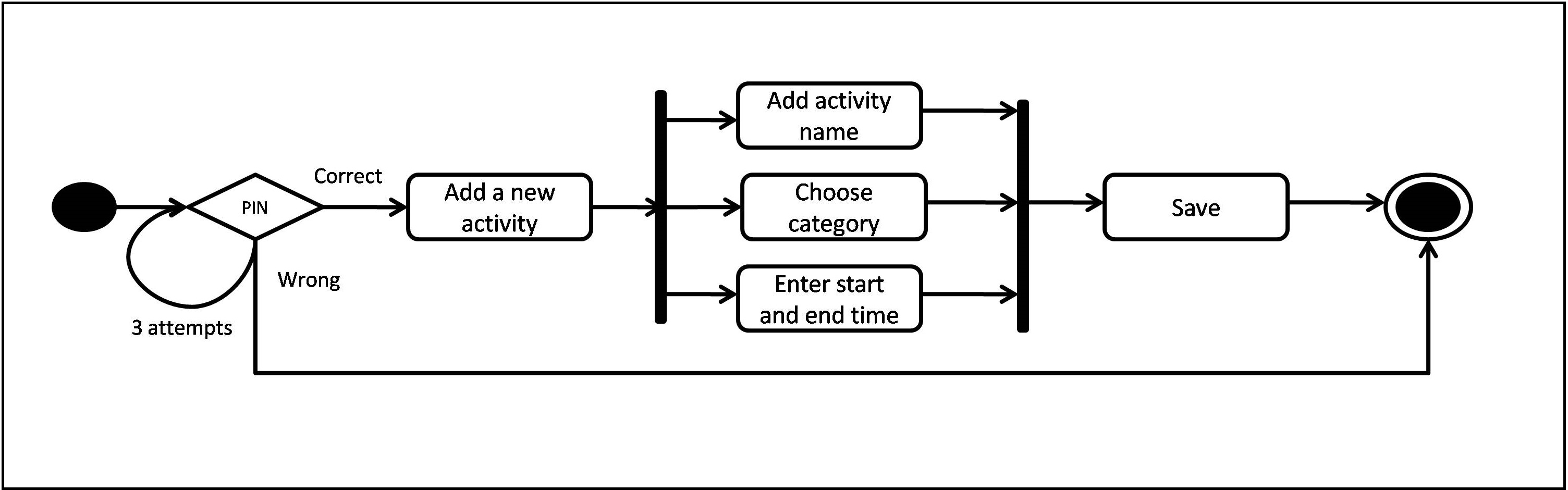
The above figure represents a Behavioral diagram for Adding a new activity. Once the user is Authenticated with the correct PIN, he goes ahead with Adding a New Activity. Next, the user adds activity details such as, Name, Category and Start time & End time. Then the user Saves the Activity within the app.
On contrary, if the PIN is wrong, the user is given 3 trials and then exited from the app.
Share over social networks
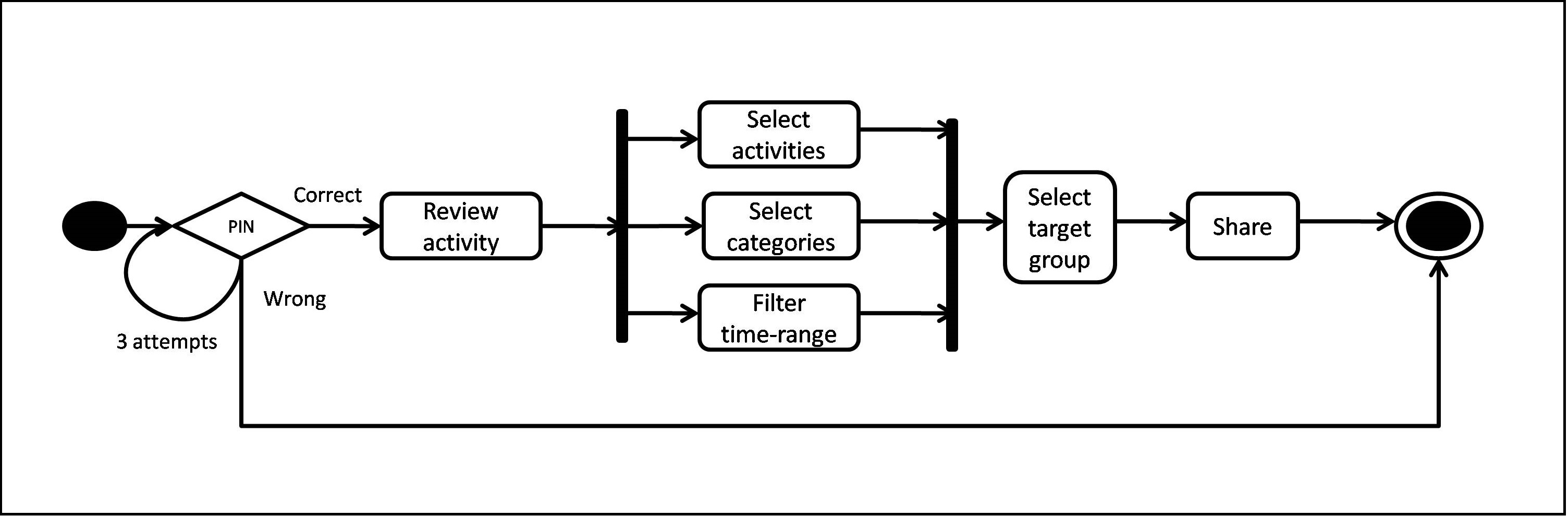
The above figure represents a Behavioral diagram for Sharing the activities over social networks. Once the user is Authenticated with the correct PIN, he chooses to Review Activities. Next, he chooses the details to share such as, Activity name, Category and Time range filter. Then the user Selects the target recipients and Social networks to share the data. Lastly the user clicks on the Share button.
On contrary, if the PIN is wrong, the user is given 3 trials and then exited from the app.
Export data
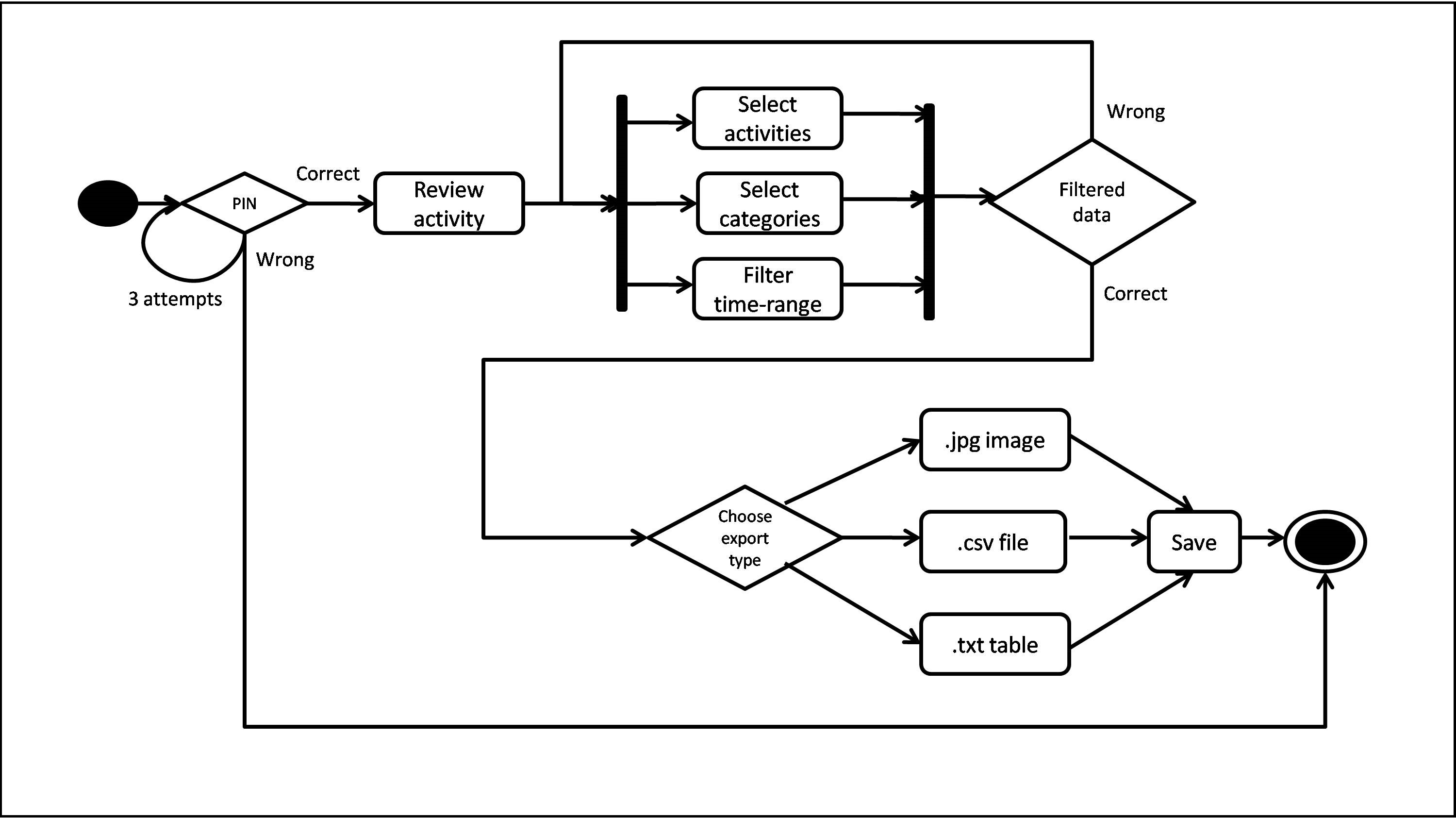
The above figure represents a Behavioral diagram for Exporting the activity data. Once the user is Authenticated with the correct PIN, he chooses to Review Activities. Next, he chooses the details to export such as, Activity name, Category and Time range filter. Then the user clicks on Export option where he is asked to choose the output type. He can choose among .jpg image file, .csv excel format spreadsheet or .txt notepad format text table. Lastly the user confirms and exports the data as desired.
On contrary, if the PIN is wrong, the user is given 3 trials and then exited from the app.
Interaction diagram
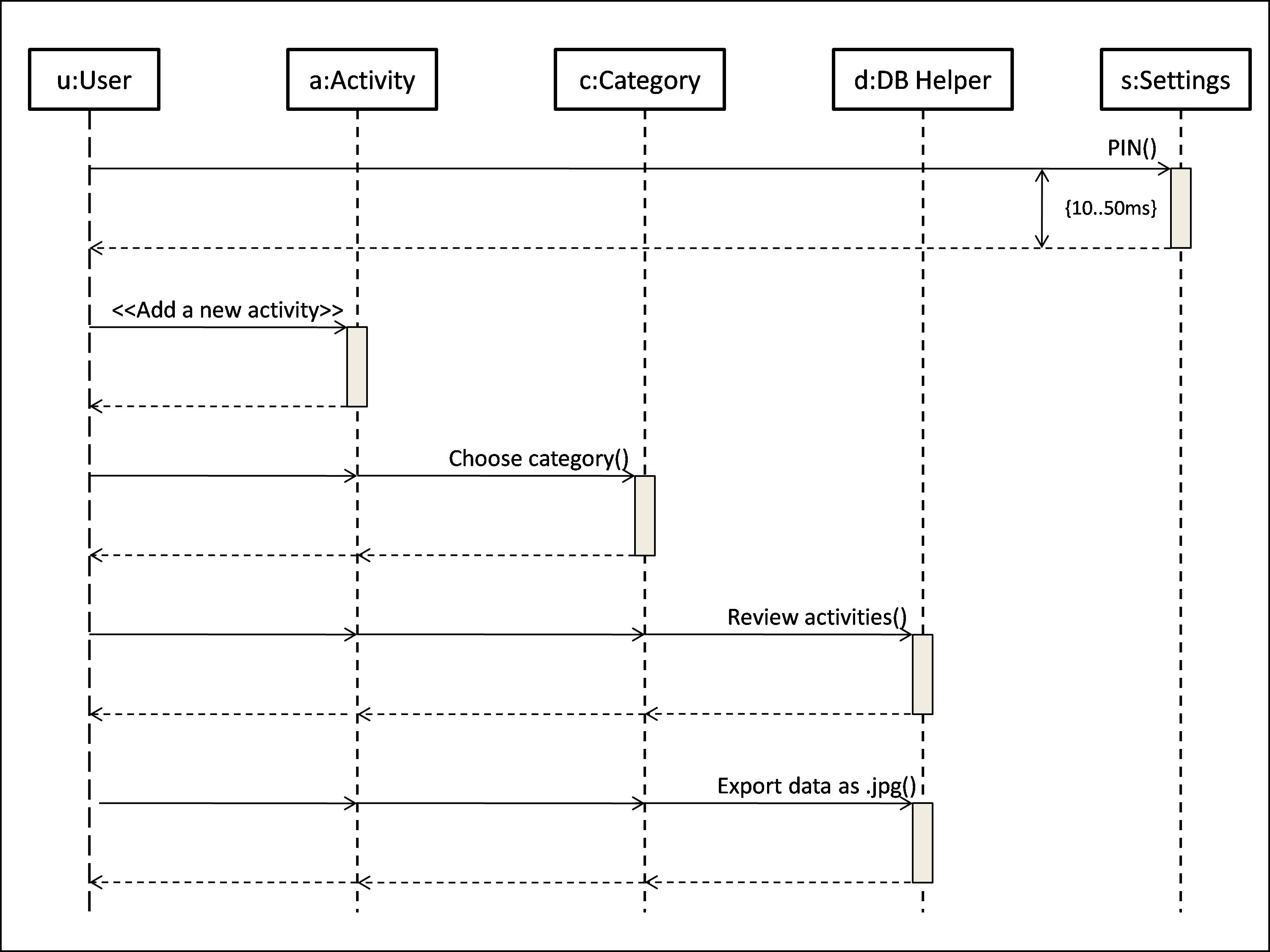
An Interaction diagram denotes the sequence of actions in an UML format. The possible flow of actions that an user attends to, for Exporting data is denoted by this figure.
5 Objects are denoted here as checkpoints along with their respective Timelines and the Messages between them. The time taken to respond to a PIN authentication is also depicted, as Duration constraint. There are 2 directional Arrows. One leading from left to right towards the Activation bar which stands for an action signal and similarly, another leading from right to left for a respond signal.
Class diagrams
A Class Diagram depicting the different functionalities of the application is shown below.
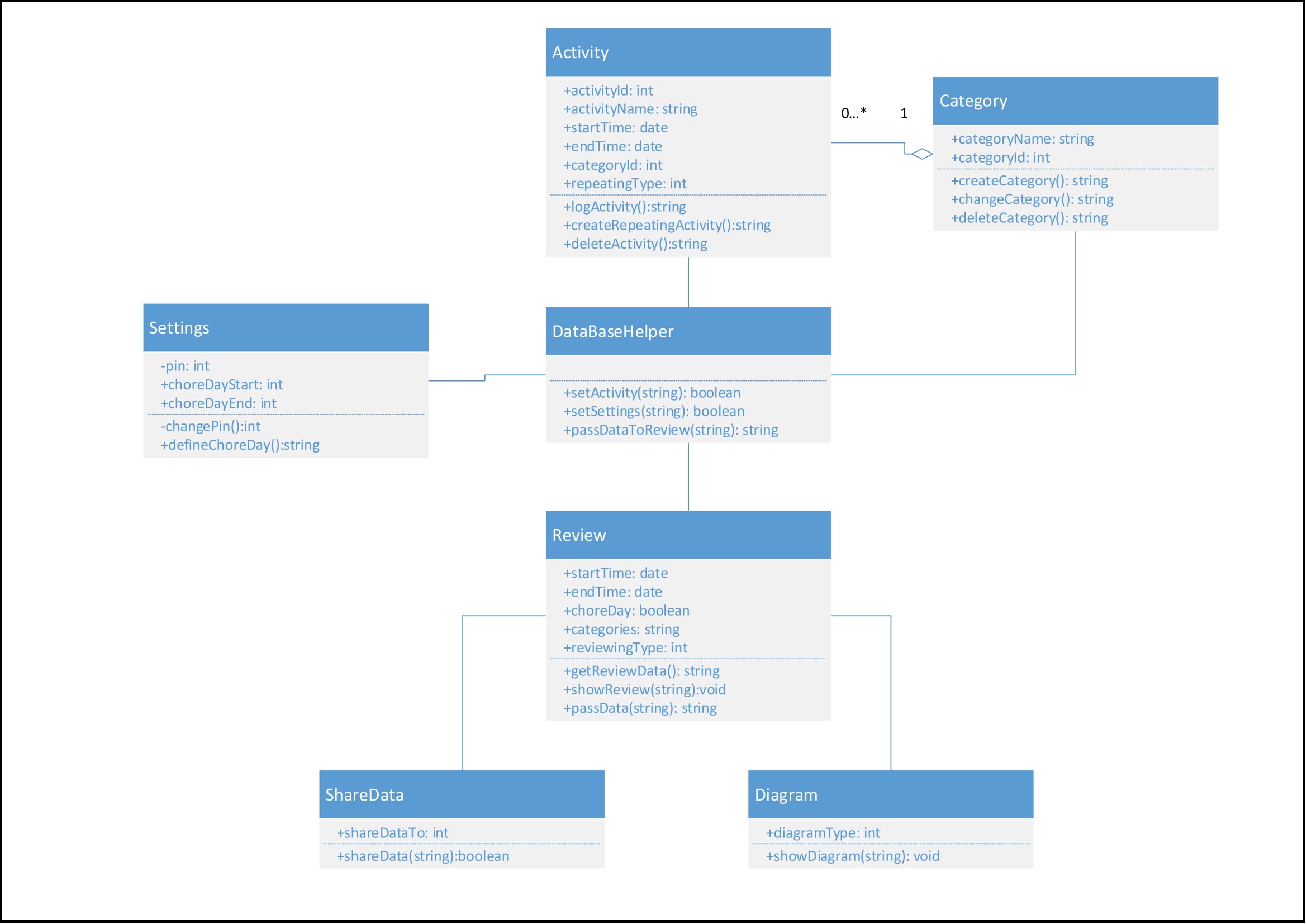
It is noticed that ‘Activity’, ‘Category’, ‘DataBase Helper’ and ‘Settings’ are our main classes. They have been mapped to the respective behavior diagrams as well.
Each class consists of the Attribute part and the Method part. The Attribute part depicts the different values used in the class and its corresponding data type. Similarly, the Method part depicts the different funtions that make use of the Attributes. It also defines the return types of the functions. Every Method can make use of either one or more than one Attributes.
As seen in the above figure, there are different ways of declaring an Attribute.
’+’ denotes a public declaration which indicates that the attributes are available to other classes as well, without restrictions.
- Examples in our application include - ‘activityName’, ‘categoryName’, ‘startTime’, ‘endTime’ etc..
’-‘ on the contrary denotes a private declaration which indicates that the attributes are secure and available within that particular class.
-
Example in our application is a PIN attribute that must not be visible outside the specific class.
-
Activity class: This class is used for capturing the activity details which are entered by the user. The activity details are for example: start date and time, category name or activity name. Also, this class will pass these values to the DataBaseHelper class.
-
Category class: This class helps managing the categories. Through it the user can define new categories and assign activities to each of them. Also, Categories can be changed and deleted. The categories will be logged into the data base through the DataBaseHelper class.
-
Settings class: This class helps managing the settings and personal data of the user. These information can be stored and changed by using this class. Additionally, this class helps securing the data with the user defined PIN. The PIN will be stored within the app, the chore day settings will be stored in the data base, which can be accessed by the DataBaseHelper class.
-
Review class: This class helps the user review their logged activities through accessing them from the data base. First, it lets the user pick the review attributes like start time and end time of the review. After that it can pass the data to the ShareData class and the Diagram class.
-
ShareData class: It receives data from the Review class and allows the user to share this data to different applications.
-
Diagram class: This class receives review data from the Review class and displays it in a diagram so the user can get an overview of his activities.
-
DataBaseHelper class: This class does not contain any attributes because it does not have any functional declarations of its own. It uses attributes from other classes and performs actions on them as necessary, such as writing activities into the database or reading them out when the user wants to review their activities.
A typical cardinality as denoted in the class diagram (the relation between “Category” and “Activity”) - A category might contain more than one activity but an activity always belongs to at least one category.
Design Pattern
Our main design pattern will be MVC (Model View Controller). There are 3 aspects of this design pattern:
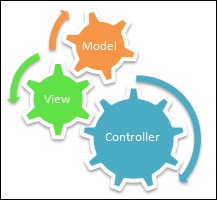
- Model: Activity, Category
- View: Activities
- Controller: DB Helper
The DB Helper is used to control all the communication with DB and also to update the views which eventually allow us keeping our concerns separate.
The reasons for choosing MVC design pattern:
- Decoupled and reusable code
- Making architectural decisions becomes easier
- Easy debugging
- Easy adaptation for the changing environment
Development strategy
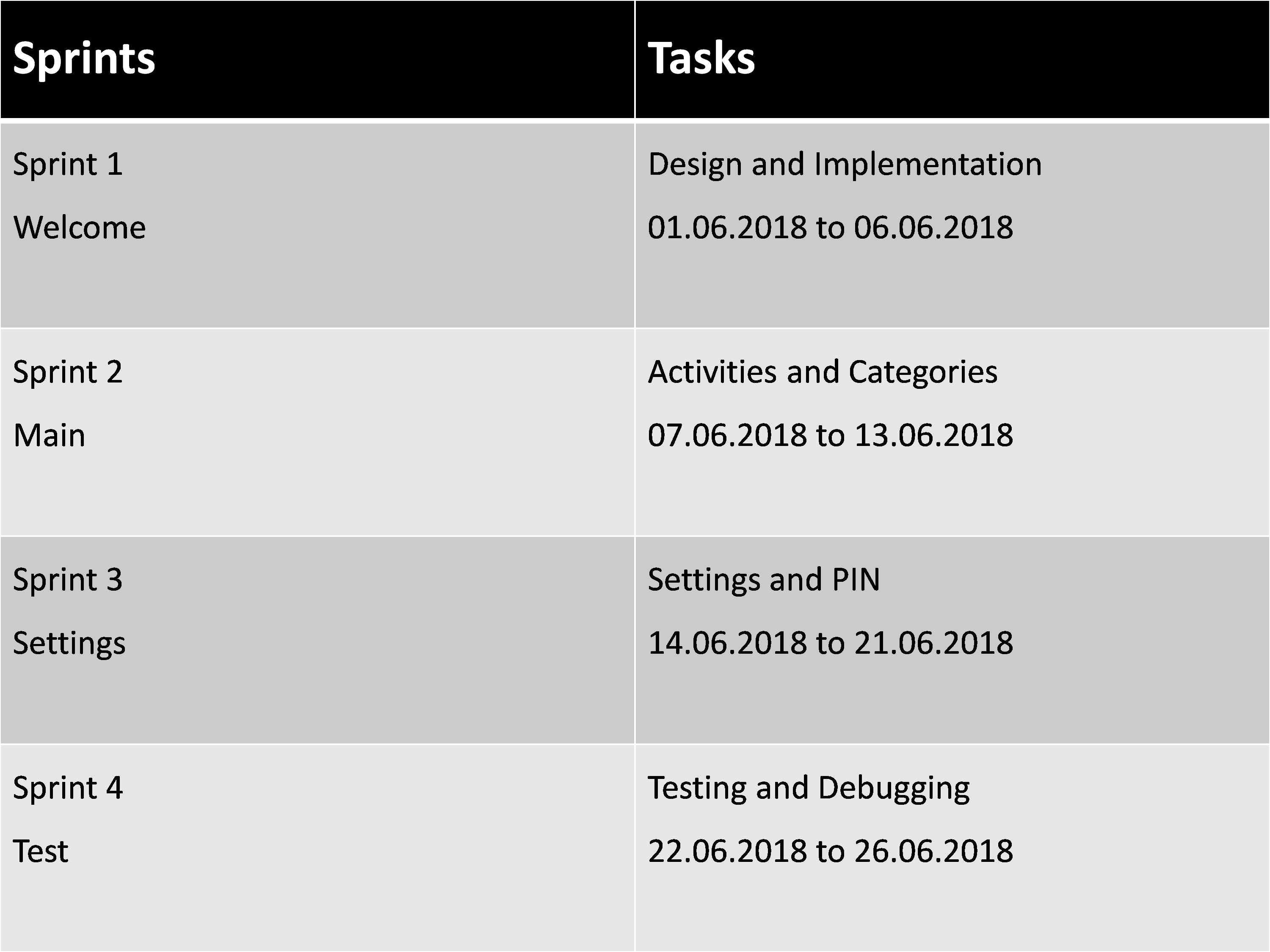
Development phase was monitored through GitHub, where we placed our user stories as the integral design parameters for the software system, depending upon the relevance of each user story it was assigned to each of the members in group and moved to ‘in progress’. Once the design was completed each user stories that was assigned to each team member was reviewed during sprints within the presence of whole team.
A shared ZenHub portal was used by the team to monitor the progress of the project. We also regularly updated the different issues we faced and maintained a schedule to meet and resolve the same.
Summary of Changes
The requirement phase was constantly updated for each meeting with our customer. It was made sure that the development team and our customer were on the same page. We ensured that the exact requirements of our customer was met.
Below are the changes that were implemented as the application development progressed.
- Our initial idea was that the application would work online on the internet but was later confirmed to be an offline application.
- The concept of adding calendar functionalities were removed as that would convert the app to an event manager instead of an activity manager.
- The focus was shifted from multiple users to a single user per application. PIN feature would be developed for a single user.
- Certain storage tweaks were made to decrease the size of the database file.
A new post on Implementation of our Design and also details of our progress is in the upcoming sprints.